1. General Concepts
1) Basic microcomputer design
집적 회로 안에 프로세서와 메모리, 입출력 버스 등의 최소한의 컴퓨팅 요소를 내장한 초소형 컨트롤러

1> Clock
- CPU에 전기적으로 공급되는 신호 (주기적으로 일정한 signal을 보내주는 칩)
- synchronizes all CPU and BUS operations
- Machine (clock) cycle measures time of a single operation
- Clock is used to trigger events
2> CU (Control unit)
coordinates sequence of execution steps
- 명령어 코드(연산 코드)를 해독(decoding) 후 필요한 제어 신호를 발생 (sequencing & execution)
- Sequencing : 마이크로 연산(micro operation)을 적절한 순서대로 처리하게 함
- Execution : 다양한 마이크로 연산(micro operation) 실행
3> ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
- 제어 장치의 지시에 따라 산술, 논리, 비트 연산등의 실제 연산을 수행하는 장치입니다.
cf> Operations inside the Computers
1> arithmetic : +, -, ×, ÷, modular
2> logical : NOT, AND, OR
2) Instruction execution cycle
1> Fetch (Fetch Instruction) : memory에 접근해서 instruction을 가져온다.
2> Decode (Decode Instruction) : Fetch 단계의 instruction(opcode)을 가져오고 해독한다.
3> Fetch operands
4> Execute (Execute Instruction) : decode된 instruction에 따라 data에 대한 연산 수행
5> Store Output : instruction에 의해 처리 완료된 data를 memory에 기록

3) Machine Instruction
1> 정의 : CPU가 하는 일
2> generic format

- op-code : operation code
- operand : 피연산자 (data or the location of the data in memory)
3> example

- 해석 : 8bit number 5(operand)를 AL register로 옮겨라(op-code)
- 어셈블리어 : mov al, 5
4> 그래서 program은 machine instruction들의 연속이다.
5> Assembly Language Instruction (3> 예시)
- Mnemonic : mov
- operand : al, 5
4) Reading from memory
1> cycle 1 : 읽고자하는 value의 address를 address bus에 둔다.
2> cycle 2 : processor의 RD(read pin)을 확인한다.
3> cycle 3 : memory chip의 반응을 위해 한 cycle 기다린다.
4> cycle 3~4 : data를 data bus에서 destination operand(particular register)로 복사한다.

5) Cache Memory
1> DRAM과 SRAM
- DRAM은 CPU 밖에 있는데 속도가 느리다. (CPU 클럭 속도를 현저히 못 따라간다.)
- 그래서 DRAM과 CPU 사이에 비싸지만 SRAM을 배치한다. SRAM이 바로 Cache Memory이다.
2> 정의 : CPU 내부와 외부에 있는 빠른 속도의 static RAM
- Level-1 cache: inside the CPU
- Level-2 cache: outside the CPU
3> Cache hit: when data to be read is already in cache memory
4> Cache miss: when data to be read is not in cache memory.
6) Multitasking

7) How programs run?

2. IA-32 Processor Architecture
1) Modes of operation
1> Protected mode
- native mode (Windows, Linux)
2> Real-address mode
- native MS-DOS
3> System management mode
- power management, system security, diagnostics
4> Virtual-8086 mode
- hybrid of Protected
- each program has its own 8086 computer
2) Basic execution environment
1> Addressable Memory
- Protected mode (4 GB, 32-bit address)
- Real-address and Virtual-8086 modes (1 MB space, 20-bit address)
cf> Register 총정리 : https://intelligentcm.tistory.com/126
(아래 register 내용보다 위 글이 더 좋습니다.)
2> General-Purpose Registers (범용 레지스터)
- 속도 최적화를 위해 CPU 내부에 마련한 저장 장소

- 32-bit General-Purpose Registers (EAX, EBX, ECX, EDX, EBP, ESP, ESI, EDI) (EAX : Extended AX)
- EFLAGS
- EIP (instruction pointer)
- 16-bit Segment Registers(CS, SS, DS, ES, FS, GS) (CS : code segment / SS : stack segment / DS : data segment)
3> Accessing Parts of Registers

- EAX의 일부가 AX이고, AX의 higher portion와 lower portion이 각각 AH, AL
- EAX 중 16byte로 AX에 접근이 가능하다. (AX도 마찬가지이다.)
- 효율적으로 register를 활용하기 위해 분할

3. IA-32 Memory Management
1) Real-address mode
- 1MB 접근 가능한 RAM
1> Segmented Memory

2> Calculating Linear Addresses
2) Protected Mode
1> Flat Segment Model
(우리가 사용할 masm)
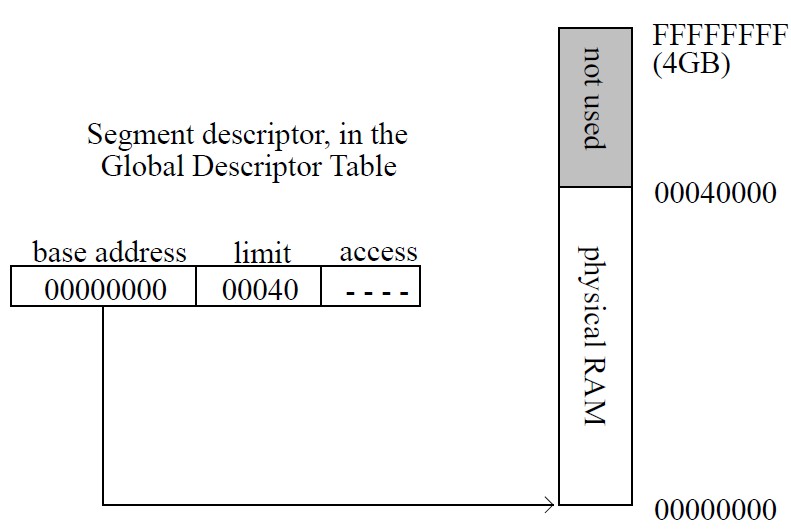
- 사용하고 있는 segment가 하나의 연속적인 공간으로 할당할 수 있게(접근할 수 있게)
(그래서 real-address mode처럼)
- segment type이 1개만 있다. (code segment할 때 그 segment)
2> Multi-Segment Model (위의 모델을 확장)
- segment type이 여러 개 있을 때

'Assembly' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4-1강 - Data Transfer, Addressing and Arithmetic 1 (Data Transfer Instruction) (0) | 2020.05.04 |
|---|---|
| 3-2강 - 어셈블리어 기본 2 (Assembly Language Fundamentals 2) - (0) | 2020.04.30 |
| 3-1강 - 어셈블리어 기본 1 (Assembly Language Fundamentals 1) - 기본 구성 요소 (0) | 2020.04.29 |
| Register 정리 (0) | 2020.04.28 |
| 1강 - 기본 개념 (Basic Concept) (0) | 2020.04.27 |


