0. Computer System Architecture
1) Motherboard
1> 중요 구성 요소
2> CPU 소켓과 RAM 소켓으로 구성 (이들은 2개의 bus로 연결되어 있다.)
2) CPU 소켓
3) RAM 소켓
1> 내부가 이진수로 되어있다. (8개의 숫자)
2> 정렬되어있다. (크기 별로)
3> Instruction, Number, Address
4) Instruction
1> load a number from RAM into the CPU
2> store a number from the CPU bank back out to RAM
CPU는 레지스터로...
레지스터가 RAM에서 받아와서 저장한다.
3> add two numbers together
4> compare one number with anoter
5> jump to another address in RAM
cf>
어떻게 해석하는가?
=> complie: translation / cpu can only understand
what complie does?
=> C++을 컴퓨터가 이해할 수 있게 변화
1. Welcome to AL
0) linker와 assembler
1> assembler : 어셈블리어에서 기계어로 바꿔주는 utility program
2> linker : assembler로 만들어진 개별적인 파일들을 하나의 실행가능한 프로그램으로 결합시켜주는 un
1) 기계어와 assembly(AL)와의 관계
1> 기계어는 cpu가 이해할 수 있는 언어
2> AL은 short mnemonic으로 진술된 statement로 구성되어있다.
- short mnemnic (ADD, MOV, SUB, CALL)
3> AL은 기계어와 일대일 관계이다.
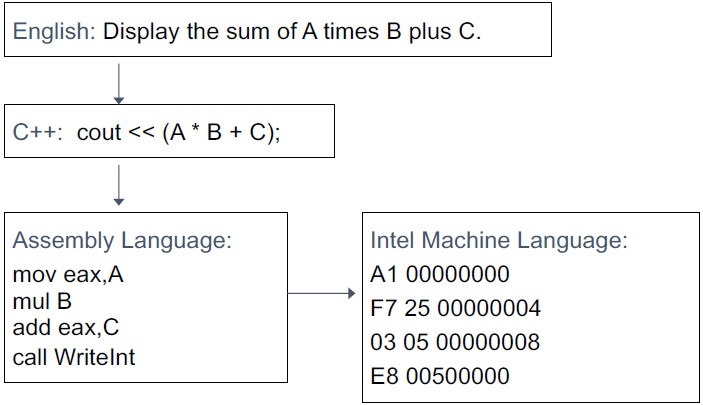
2) C++과 AL이 어떤 관계가 있나?
1> C++과 같은 high-level language는 AL이나 기계어와 일대다 관계가 있다.
2> example

(mov는 마치 '='과 같다.)
(register에는 값이 하나씩 저장되어 있다.)
3) AL은 portable한가?
1> portable
해당 언어의 source program이 다양한 computer system에서 compile과 실행이 될 수 있다.
(C++은 그러하다.)
2> AL is not portable
- 특정 processor family를 위해 만들어졌다.
- processor family에 따라 assembly 언어가 다르다.
2. Virtual Machine Concept
1) 가상 머신
1> 모든 hardware에서 직접 실행되는 L0를 가진다.
2> L1으로 만들어진 program은 2가지 방식으로 실행
- 해석 : L0은 L1을 해석하고 실행한다.
- 번역 : L1은 L0로 번역되고 computer hardware에서 실행한다.
2) Specific Machine Levels

1> High-Level Language (Level 5)
ex> C++, Java, Pascal, Visual Basic
2> Assembly Language (Level 4)
- 어셈블리는 인간이 다룰 수 있는 낮은 수준의 언어이다.
- Instruction mnemonics가 기계어와 일대일 대응이다.
(mnemonic : 어셈블리 언어에서 더하기를 나타내는 애드(ADD)나 곱하기를 나타내는 멀(MUL) 따위의 명령 코드)
3> Operating System (Level 3)
- Provides services to Level 4 programs
- Translated and run at the instruction set architecture level (Level 2)
4> Instruction Set Architecture (Level 2)
- Machine Language를 의미
- Also known as conventional machine language
- Executed by Level 1 (microarchitecture) program
5> Microarchitecture (Level 1)
- Interprets conventional machine instructions (Level 2)
- Executed by digital hardware (Level 0)
6> Digital Logic (Level 0)
- CPU, constructed from digital logic gates
- System bus and memory
- Implemented using bipolar or MOS transistors
3. Data Representation
1) Binary Numbers
1> digit은 1과 0이 있다.
- 1 = true
- 0 = false
(number 는 123 (백이십삼) 이라는 숫자를 의미합니다. 우리가 일반적으로 사용하는 숫자 입니다.
digit 는 아라비아 숫자 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. 0 자체를 의미)
2> MSB, LSB
– MSB : most significant bit
– LSB : least significant bit

3> translation (unsigned decimal -> binary)
- 2씩 나눠가며 그 나머지를 기록하면 된다.

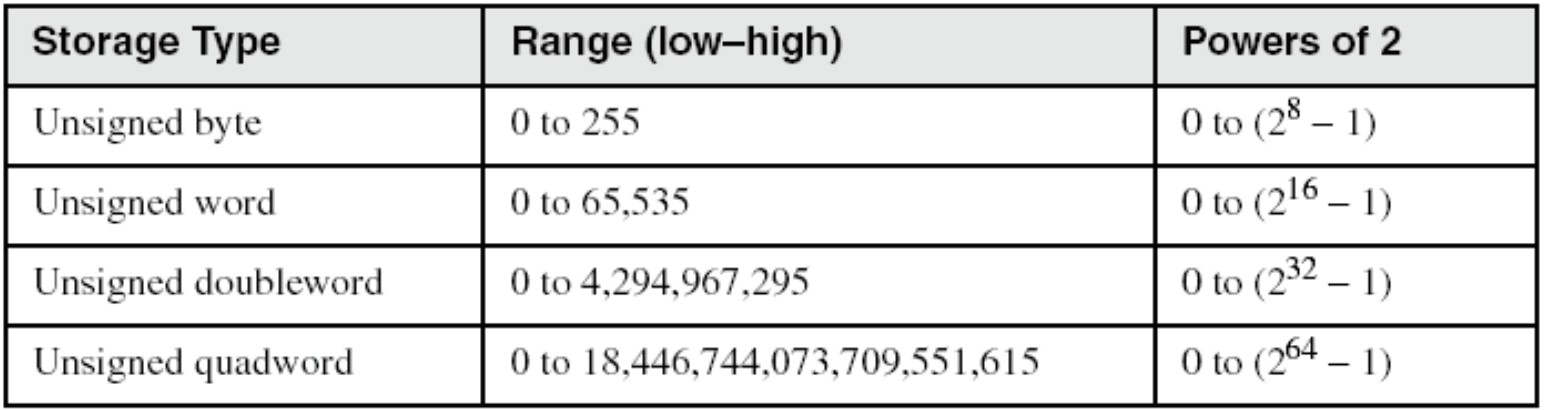
2) Integer Storage Size
1> standard size
byte = 8 / word = 16 / doubleword = 32 / quadword = 64
2> unsigned integer의 표현 범위
3) Hexadecimal Integers
1> binary value와의 관계

2> translation (binary -> hexadecimal)
- binary에서 4자리가 hexadecimal 1자리와 대응된다. (반대의 경우도 마찬가지 원리로 진행한다.)
- 예제

3> translation (hexadecimal -> decimal)
16의 거듭제곱과 각 계수들을 곱하는 단순 연산
4> translation (decimal -> hexadecimal)
이전에 binary로 변환할 때처럼 16으로 나눈 나머지를 계속해서 기록한다.

4> Hexadecimal Addtion & Subtraction
- hexadecimal subtraction이 필요한 이유 예제 (address에서 변수가 사용한 메모리 구함)

현재까지의 규칙으로는 음의 값을 표현하지 못한다. 그래서 부호만 나타내는 bit를 마련했다.
4) Signed Integers
1> 맨 앞자리는 부호를 나타내는 bit이다. (부호가 MSB에 위치하게 된다.)
- 0 = positive
- 1 = negative
2> 예상되는 문제점

- 1번의 경우 postitive 0과 negative 0으로 2개의 0이 존재한다.
- 2번의 경우 양수와 음수의 덧셈이 이상하다.
3> 음수 표현법
(a라는 양수의 음수 구하는 법)
- [1] 먼저 해당 양수 a의 보수를 구한다.
- [2] 그 보수에 1을 더한다
ex>
a = 0010 -> [1] 1101 -> [2] 1110
4> 음수에 관한 몇가지 성질
- 1111 = -1
- 음수가 작아질수록(절댓값이 커질수록) 맨 앞자리를 제외한 나머지 자리는 수의 크기가 감소
5> hexadecimal의 경우 맨 앞 자리 부호가 7보다 크면 음수이다.
6> signed integer의 범위

5) Character Storage
알파벳을 어떻게 컴퓨터로 저장하는가? ASCII
1> ASCII
- 8bit code (7bit를 쓰면 standard ASCII / 8bit를 쓰면 Exteded ASCII)
- character
- 0 - 31 : control character
- 32 - 127 : normal character
- 128 - 255 : graphic symbols and greek character
- 기억할 ASCII
- '0' : 30h (48)
- 'A' : 41h (65)
- 'a' : 61h (97)
2> Control Characters
- 0 ~ 31의 ASCII code
- standard outpuu으로 출력하면 predefined action을 취한다.

4. Boolean Operations
1) Boolean Algebra
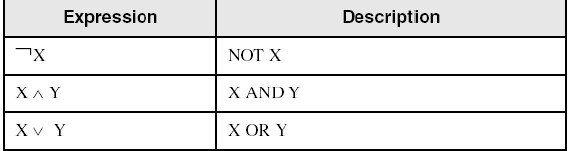
1> NOT

2> AND

3> OR

'Assembly' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 4-1강 - Data Transfer, Addressing and Arithmetic 1 (Data Transfer Instruction) (0) | 2020.05.04 |
|---|---|
| 3-2강 - 어셈블리어 기본 2 (Assembly Language Fundamentals 2) - (0) | 2020.04.30 |
| 3-1강 - 어셈블리어 기본 1 (Assembly Language Fundamentals 1) - 기본 구성 요소 (0) | 2020.04.29 |
| Register 정리 (0) | 2020.04.28 |
| 2강 - X86 Proceesor Architecture (0) | 2020.04.28 |


