0. STL
1> 표준 라이브러리 (Standard Template Library)
2> 프로그램에 필요한 자료구조와 알고리즘을 Template로 제공하는 라이브러리
1. Sort 함수
1) 특징
1> '#include <algorithm>'을 선언해야 한다.
2> quick sort를 기반으로 함수가 구현되어 있어서
3> 시간복잡도가 O(nlogn)이다.
2) 사용법 기본
sort(start 주소, end 주소)
1> [start, end) 범위에 있는 element들을
- start를 포함하고 end를 포함하지 않는 구간
- 그러니 정렬하고 싶은 범위보다 하나 더 뒤에 있는 원소의 주소까지 argument에 넣어야 한다.
2> 오름차순(default)으로 정렬한다.
3) 다른 사용 예시
1> array
sort(arr, arr+n);
2> vector
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
- v.begin()은 vector의 시작원소를 가리키지만
- v.end()는 vector 마지막 원소의 다음 원소를 가리킨다.
3> 다른 기준으로 정렬
sort(start 주소, end 주소, 정렬 함수);
4> 내림차순
sort(start 주소, end 주소, greater<'자료형'>());
cf> 다른 기준으로 정렬 예시
bool compare(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
// True가 되도록 정렬 == a가 b보다 크도록 정렬 == 큰 값이 앞에 온다.
}
int main()
{
int a[10] = {7, 3, 5, 4, 1, 9, 10, 8, 2, 3};
sort(a, a + 10, compare);
}
// 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
2. 다른 방식으로 응용
1) 특정한 변수를 기준으로 정렬할 것
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
class Student
{
public:
string name;
int score;
Student(string name, int score)
{
this->name = name;
this->score = score;
}
bool operator < (Student &student)
{
return this->score < student.score;
}
};
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
Student students[] =
{
Student("가", 60),
Student("나", 92),
Student("다", 56),
Student("라", 77),
Student("마", 100)
};
sort(students, students + 5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << students[i].name;
}
}
cf> vector 사용법
1) 사용법
1> 헤더 파일: '#include <vector>' 선언
2> 선언: 'vector<'자료형'> '변수 이름'
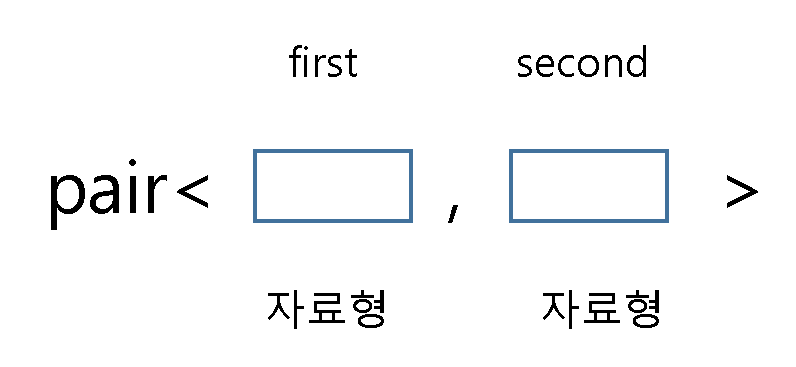
cf> pair
1) 사용법
1> 헤더 파일: '#include <utility>' 선언
2> 선언: 'pair<'자료형1', '자료형2'> '변수 이름'
2) indexing
2) pair와 vector를 이용한 sort
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int MAX = 1000;
bool compare(pair<string, pair<int, int>> a, pair<string, pair<int, int>> b)
{
if (a.second.first == b.second.first) return a.second.second > b.second.second;
else return a.second.first > b.second.first;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
vector <pair<string, pair<int, int>>> v;
v.push_back(pair<string, pair<int, int>>("가", make_pair(90, 177)));
v.push_back(pair<string, pair<int, int>>("나", make_pair(77, 168)));
v.push_back(pair<string, pair<int, int>>("다", make_pair(83, 171)));
v.push_back(pair<string, pair<int, int>>("라", make_pair(60, 178)));
v.push_back(pair<string, pair<int, int>>("마", make_pair(100, 180)));
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i].first << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
'알고리즘 > 알고리즘_기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 10강 - 큐 (Queue) (0) | 2020.03.11 |
|---|---|
| 9강 - 스택 (Stack) (0) | 2020.03.11 |
| 5강 - 병합 정렬 (Merge Sort) (0) | 2020.03.11 |
| 4강 - 퀵 정렬 (Quick Sort) (0) | 2020.03.11 |
| 3강 - 삽입 정렬 (Insertion Sort) (0) | 2020.03.11 |


