2. Defining and Using Procedures
1) Creating Procedures
1> 다른 language의 함수와 유사한 개념이다. (큰 문제를 작은 문제로 쪼개어 다룬다.)
2> 사용
func_name PROC
.
ret
func_name ENDP
2) Documenting Procedure
(procedure 만들 때 적어주면 좋은 것들)
1> procedure가 수행하는 작업에 대한 설명
2> Receives : Input parameters에 대한 설명 (their usage and requirements)
3> Returns : procedure가 return하는 값들에 대한 설명
4> Requires : procedure가 호출되기 전에 만족되어야 하는 조건들(precondition)에 대한 설명
5> 예시
SumOf PROC
; Calculates and returns the sum of three 32-bit integers.
; Receives: EAX, EBX, ECX, the three integers. May be signed or unsigned.
; Returns: EAX = sum, and the status flags (Carry, Overflow, etc.) are changed.
; Requires: nothing
add eax,ebx
add eax,ecx
ret
SumOf ENDP
3) CALL, RET (Instruction)
1> CALL : procedure를 호출
- 다음에 실행될 instruction의 주소를 stack에 push
- 호출되는 procedure의 주소를 EIP에 copy
2> RET : procedure에서 return
- stack의 top을 EIP로 pop
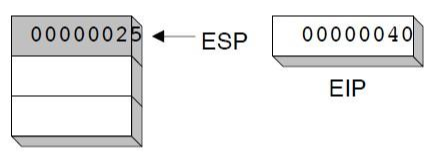
3> 예시 1
main PROC
00000020 call MySub
00000025 mov eax,ebx
.
main ENDP
MySub PROC
00000040 mov eax,edx
.
ret
MySub ENDP- 00000020 call MySub : 다음에 실행될 instruction(MOV)의 주소(00000025)를 stack에 push
- 00000020 call MySub -> 00000040 mov eax,edx : 호출되는 procedure(MySub)의 주소(00000040)를 EIP에 copy
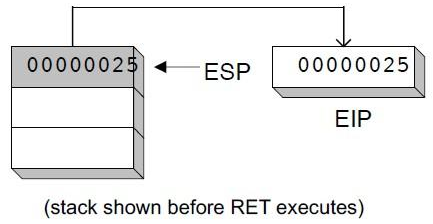
- ret : stack의 top(0000025)을 EIP로 pop
4> 예시 2 : Nested Procedure Call
main PROC
.
.
call Sub1
exit
main ENDP
Sub1 PROC
.
.
call Sub2
ret
Sub1 ENDP
Sub2 PROC
.
.
call Sub3
ret
Sub2 ENDP
Sub3 PROC
.
.
ret
Sub3 ENDP- 위와 같이 4중 중첩인 경우 stack에 3개의 return address가 저장된다.
- main -> sub1 -> sub2 순서대로 stack에 쌓인다.

4) Local and Global Labels
1> local label은 procedure 내에서만 접근 가능하다.
2> global label은 어디서나 접근이 가능하다.
3> 예시
main PROC
jmp L2 ; error
L1: ; global label
exit
main ENDP
sub2 PROC
L2:
jmp L1 ; local label
ret ; ok
sub2 ENDP
5) Procedure Parameters
1> procedure는 다른 여러 프로그램들에서 사용될 수 있기 때문에 specific한 변수명을 필요로 하면 안된다.
=> parameter는 runtime에 결정되어서 다양한 곳에서 필요한 procedure를 유연하게 할 수 있다.
2> not flexible procedure (안 좋은 사례)
ArraySum PROC
mov esi, 0 ; array index
mov eax, 0 ; set the sum to zero
mov ecx, LENGTHOF myarray ; set number of elements
L1: add eax, myArray[esi] ; add each integer to sum
add esi,4 ; point to next integer
loop L1 ; repeat for array size
mov theSum,eax ; store the sum
ret
ArraySum ENDP- 위 프로그램은 myArray, theSum이라는 specific 변수에 대해서만 작동한다.
3> flexible procedure (좋은 사례)
ArraySum PROC
; Receives: ESI points to an array of doublewords,
; ECX = number of array elements.
; Returns: EAX = sum
;-----------------------------------------------------
mov eax, 0 ; set the sum to zero
L1: add eax, [esi] ; add each integer to sum
add esi,4 ; point to next integer
loop L1 ; repeat for array size
ret
ArraySum ENDP- 이 procedure는 ESI에 주소가 들어있는 임의의 DWORD array의 합을 EAX에 저장한다.
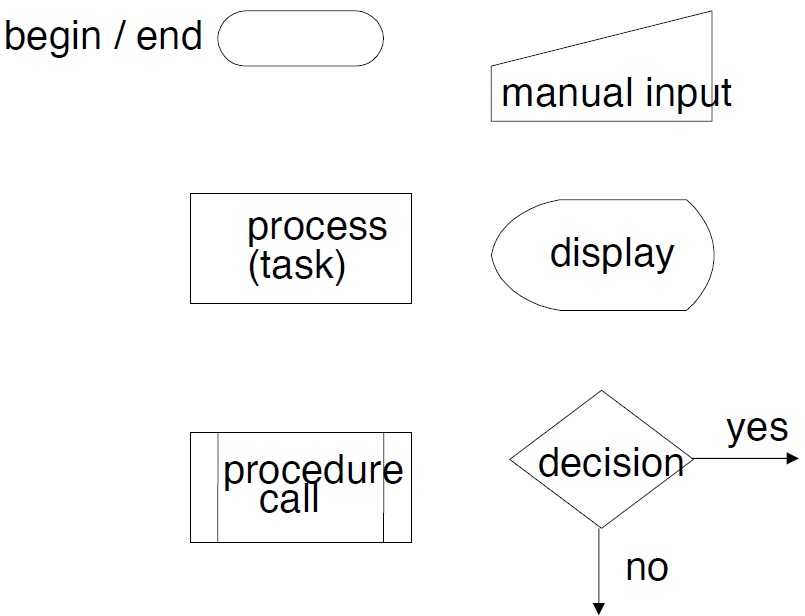
6) Program Design Using Flowchart
1> Basic building blocks of flowcharts
2> 예시 1 : 이전에 배운 ArraySum procedure

push esi
push ecx
mov eax,0
AS1: add eax,[esi]
add esi,4
loop AS1
pop ecx
pop esi3> 예시 2
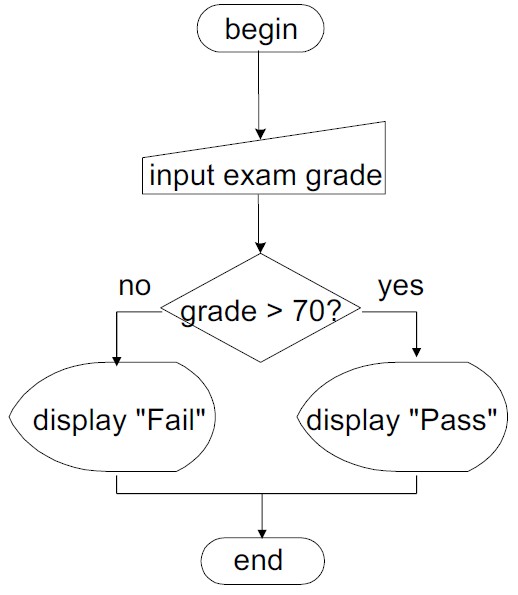
input exam grade from the user
if( grade > 70 )
display "Pass"
else
display "Fail"
endif
7) USES (operator)
1> 보존해야할 register를 명시
2> 예시
ArraySum PROC USES esi ecx
mov eax,0 ; set the sum to zero
etc.MASM은
위의 USES esi ecx 부분을
push esi
push ecx
pop ecx
pop esi
로 변환한다.
3> 변환되었을 경우의 코드
ArraySum PROC
push esi
push ecx
mov eax, 0
. . .
pop ecx
pop esi
ret
ArraySum ENDP8) register를 push하지 말아야하는 경우
SumOf PROC ; sum of three integers (EAX = 1, EBX = 2, ECX = 3)
push eax ; line 2 : stack EAX = 1
add eax,ebx ; line 3 : EAX = 3, EBX = 2
add eax,ecx ; line 4 : EAX = 6, ECX = 3
pop eax ; line 5 : stack EAX = 1
ret
SumOf ENDP- line 4에서 3개의 register의 합인 6이 EAX에 저장되지만
- line 5에서 이전에 stack에 EAX를 저장해둔 값을 다시 가져와서 초기값 1로 되돌아 간다.
cf> Program Design Using Procedures
Top-Down Design (functional decomposition)
- 코드를 작성하기 전에 프로그램을 디자인 함
- 큰 작업을 작은 작업들로 나눔
- 프로시저 호출에 의한 계층적 구조 사용
- 각각의 프로시저 테스트
cf> 어셈블리는 반환형을 특별히 특정할 필요가 없다.
어떤 register에 return값이 들어가있다 정도만 중요하다.


